Starting an online business can be exciting as there are heaps of business ideas to choose from.
But it can also be somewhat of a tough grind to navigate through the various options and find the right fit for you.
Today, I’m going to make things really easy for you:
I’ll show you the seven universal categories of online business models into which all online businesses fall.
By getting a bird’s eye view of the different types of online businesses, it will become easier for you to decide which one to create.
7 Major Online Business Models
While there are thousands of ways to make money online, some online business ideas are more sustainable and viable than others.
For starters, when looking for an online business idea, you’d likely come across several lame suggestions like “take surveys and earn rewards,” “get paid for matched betting,” and “surf the web/watch videos for $2.”
The thing is that these kinds of suggestions are either arrant scams or are not sustainable at the least.
Here’s the ultimate formula for knowing a sustainable, viable online business:
Every sustainable, profit-making online business is predicated on value.
What this means is that to make money online in a sustainable way, you should be providing value in one way or another in exchange for money.
Doing business online is not entirely different from doing business offline. In the traditional, brick-and-mortar setting, you make money by offering real-world value to other people or businesses.
It’s the same online, except it is done primarily through digital technology.
With that in mind, if you’re serious about making money online, there are seven major online business models that work.
All sustainable, legitimate online businesses are categorized under these seven universal categories:
- Content-based business model
- Freelancing business model
- Knowledge-based business model
- Non-content-based digital product business model
- eCommerce (physical product) business model
- Software-based business model
- Virtual assets business model
I’ll explain each of these in detail and also show you the limitations associated with each of the models. This should hopefully help you make a more informed decision on which one to start.
1. Content-based Business Model
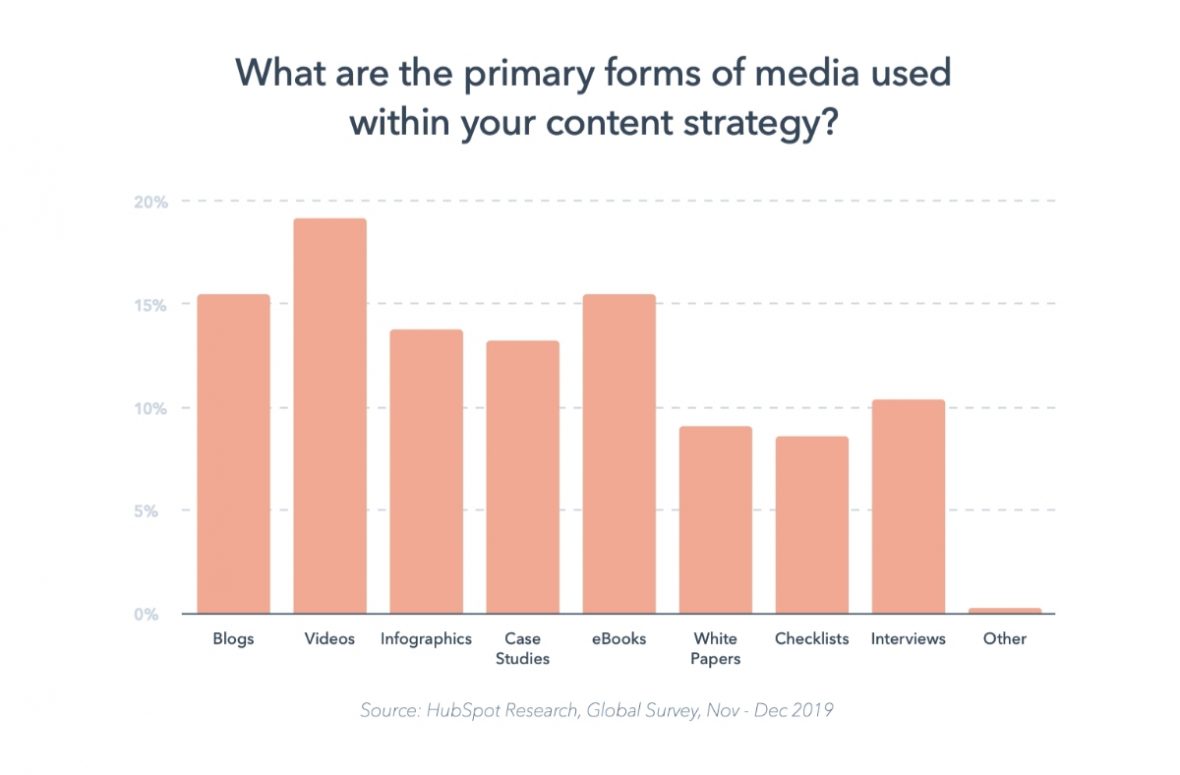
A content-based online business model is a strategy in which you primarily generate income by creating and distributing valuable content.
This content can take various forms, including articles, blog posts, videos, podcasts, online courses, marketing emails, eBooks, gated content, informational social media content, webinars, online workshops, and more.
The goal is to attract and engage a target audience, ultimately driving profitable customer actions.
Examples of Content-based Businesses
Here’s a look at some content-based online business examples (plus the relevant monetization strategies)
| TYPE | MONETIZATION METHODS |
|---|---|
| Online courses | One-off payments or split payments |
| Blogging | Affiliate marketing, Pay-per-click ads, sponsored posts, ad space, premium content, paid speaking, paid conferences, paid webinars |
| Vlogging | Brand sponsorship, YouTube Partner Program, affiliate promotions, Google AdSense |
| Podcasts | Affiliate promotions, brand sponsorship, paid speaking, premium content, paid conferences |
| eBooks | One-off purchases |
| Membership sites | Recurring subscriptions |
| Webinars and live workshops | Sponsorship, product announcement, affiliate marketing |
| Social content (e.g TikTok, Instagram, etc.) | Social ads, brand promotion, affiliate promotions, brand sponsorship |
Is the Content-based Business Model Right for You?
For the most part, content-based businesses are very easy and cheap to start. You can even start for absolutely free.
The major demanding factor is the development of content.
Why? Because in this business model, your content is your product.
From ideation to creation, content development needs attention. Big, fat attention.
It could be developing your online course, writing blog posts, recording YouTube or TikTok videos, designing Pinterest pins, or creating just any content that’s relevant to your particular content strategy.
So if you’re ready to create content, this business model might be for you.
Needless to say you have to make your content compelling and of the best quality.
For certain content-based businesses like those that require written content, faceless videos, or social media graphics, it’s possible to outsource the work, but it costs money and may still require a bit of planning from your end.
Additionally, certain content-based businesses, such as online courses, demand upfront investment in content creation. This means dedicating significant initial time and effort to crafting the material. In contrast, other content-based businesses, like social media and blogging, require ongoing content updates to maintain engagement and relevance.
One of the advantages of the content-based model is that whether you frontload the effort in the beginning or consistently upload content over time, it can keep generating traffic and/or income for months and years to come automatically.
In fact, outside of content development, almost every other aspect of a content-based business runs on autopilot.
2. Freelancing Business Model
The freelancing online business model refers to a type of work arrangement where an individual, often referred to as a freelancer or independent contractor, offers their services to clients on a project-by-project, short-term basis, rather than being employed by a single company on a long-term basis.
Freelancers are typically self-employed and work independently, providing services in various fields such as writing, graphic design, programming, marketing, and countless other services that can be sold online.
This model primarily involves using your skills to do something for other people or businesses, which is why it is also known as the skill-based service business model.
Freelance service-based businesses are monetized with service charges — your clients pay whatever fees you both agree. It could be project-based rates, hourly rates, daily rates, per-piece rates, monthly retainer, or value-based rates.
The internet has opened up a world of possibilities for people with skills to sell their services online. For instance, I started my online business career way back in 2013 selling my services as a freelance writer.
Whether you’re a writer, graphic designer, programmer, or accountant, there are countless opportunities available that you can take on as a freelancer to make money.
In short, as long as you can DO it, then you can SELL it.
Fiverr is the best place to start.
One advantage of a skill-based business is that you have the freedom to set your own rates and choose the type of work you want to do.
Examples of Freelancing Businesses
- Writing and content creation
- Web, mobile, and software development
- Design and creative services
- Administrative and virtual assistance
- Marketing and advertising services
Is the Freelancing Business Model Right for You?
Offering a service online is a great way to earn money doing what you love. The major downside to this model is that it is tactically unscalable.
The service you sell is directly attached to your skills. Which means you need to ‘be there’ to sell it. You’re basically selling your time for money.
There are only so many hours in the day and only one of you. If you stop putting in the work, the payment alerts stop coming.
So by the nature of how skill-based freelancing business works, this model puts a massive ceiling over how much you could make. Zero scalability chances!
Plus, it can also put a big manacle on your flexibility.
Want to go walk the beach with your date in the middle of the day? Too bad, you have to deliver a mockup at 2pm. Want to go on a spontaneous 2-week trip to Dubai? Well, your clients are still hard at work and would be needing your business. Or at least you’d have to reschedule 12 meetings.
3. Knowledge-based Business Model
The knowledge-based online business model involves providing expert advice and knowledge to help others achieve their goals.
Think of it as a close cousin of freelancing, but one that blurs the lines between content-based and skill-based business models.
There are two main types of knowledge-based business models:
- Consulting: a knowledge-based business model where an expert provides advice and guidance to individuals, teams, or organizations in a variety of fields such as business, finance, marketing, technology, and healthcare.
- Coaching: a knowledge-based business model where an expert helps their clients or students improve their performance or achieve their goals.
This model can be monetized in a variety of ways, such as:
- Project fees: Consultants charge a fee for each project they complete.
- Hourly fees: Consultants charge an hourly rate for their time.
- Retainer fees: Consultants charge a monthly or annual fee for their ongoing services.
- Success fees: Consultants charge a percentage of the client’s savings or profits.
Examples of Knowledge-based Businesses
- All kinds of online consulting
- All kinds of online coaching
- Business advisory services
- Group coaching
- Mastermind groups
Is the Knowledge-based Business Model Right for You?
The knowledge-based business model can be a great way to earn a good living and share your knowledge and expertise with others. However, it is important to deliver results.
So, if you’re confident in your knowledge or expertise and can demonstrate the practical application of it to help others achieve their goals, the knowledge-based business model could be an excellent fit for you.
4. Non-content-based Digital Product Business Model
This is about creating and selling digital products that are not content. In this space, the focus shifts from information or knowledge to tangible digital goods.
Think printables, stock images, templates, themes, and presets—digital creations designed to enhance, simplify, or beautify various aspects of life or business.
Unlike content-driven models, the emphasis lies in the visual impact, functional utility, or practicality of the product.
One of the beauties of this model is its scalability. Once created, these digital products can be sold repeatedly without the need for ongoing production efforts. It’s a one-time investment that continues to generate revenue, providing a passive income stream for the creator.
Non-content-based downloadables can be sold in the following ways:
- Individual Sales: Selling products individually, allowing customers to choose and purchase specific items.
- Bundled Packages: Creating packages or bundles to offer a variety of complementary digital products at a discounted rate.
- Subscription Models: Introducing subscription-based access to a library of digital downloadables with regular updates.
Examples of Non-content-based Digital Downloadables
- Printables such as planners, organizers, wall art, and so on.
- Stock images
- Templates for presentations, graphics, websites, and more.
- Themes for websites, blogs, or social media platforms.
- Presets
- Illustrations
- Sound effects and music loops
- Stock footage and video clips
- 3D models and textures
- Fonts and typography packs
Is the Non-content-based Digital Downloadable Model Right for You?
This model is ideal for creative minds who thrive on artistic expression and/or functional creativity. If you enjoy crafting digital products that can enhance the life or business of your audience, non-content-based digital downloadables provide a lucrative avenue.
Keep in mind that while the production cost of digital downloadables is relatively low compared to physical products, there might be initial investments in software, tools, or resources needed to create high-quality products.
Also, to maintain sales momentum, consistent marketing efforts are necessary.
However, just like its content-based counterpart, this online business model can keep generating passive income for months and years to come once you’ve created your product.
5. E-Commerce (Physical Product) Business Model
Real-world, tangible products are native to brick-and-mortar businesses but eCommerce has completely turned that on its head. It is a classic example of taking a classic business model and reinventing the wheel on it.
These days, pretty much any physical product can be sold online – tech gadgets, fashion items, artworks, household items, or just about any legitimate physical good.

And in fact, online retailing comes in many forms.
First, there’s the option of selling on a popular online marketplace such as eBay, Alibaba, or Amazon:

You basically create a virtual store within the marketplace, upload your product photos, and hopefully close some sales. (Whispers: it’s usually a lot more complicated than that.)
While some online marketplaces tend to allow the sale of general merchandise, there are niche-specific marketplaces for different industries. For instance, Etsy is a popular online marketplace that focuses on handmade products, vintage items, and the like.
The second option is selling on your own hosted online store — whether by building a store off of an existing website or creating an online eCommerce website for the sole purpose of selling the products.
For instance, you can build an online store using Shopify or WooCommerce.
This is also where eCommerce models like dropshipping and print-on-demand come under.
Here’s an example from Alex (Supercar Blondie) who leverages her online automotive authority to sell branded caps, t-shirts, and hoodies.
And then, there’s social commerce, which is the selling of products on social media.
Social commerce is a growing trend:
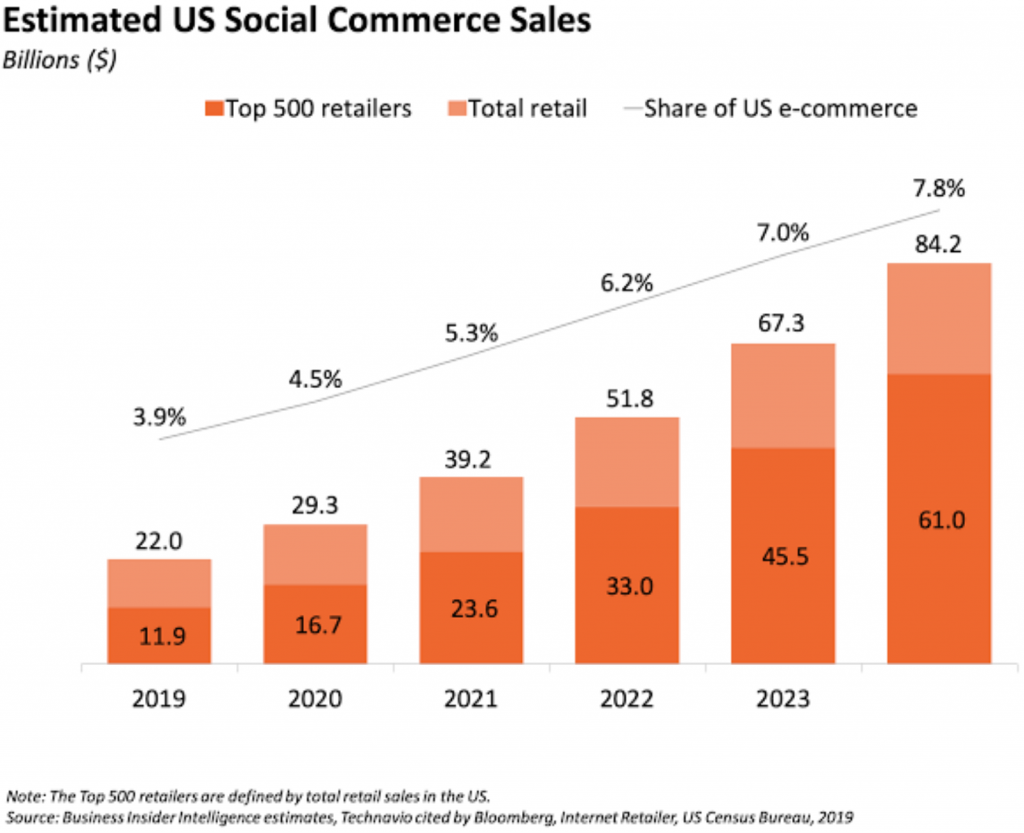
You can sell physical products on TikTok Shop, Pinterest, Facebook Marketplace, Instagram, etc.
As a case in point, it’s no secret that Kylie Jenner leverages her millions of social media followers to promote her make-up and cosmetic products.
Kylie Cosmetics also runs a stand-alone hosted online store as well as an Amazon store for her products.
This means it’s possible to combine all three strategies — marketplace, hosted, and social — to sell physical products online.
Examples of eCommerce Businesses
- Selling on eCommerce marketplaces such as Amazon
- Selling on independent online stores using a platform like Shopify
- Social commerce
- Dropshipping
- Print-on-demand
- Subscription box
Is the Physical Product eCommerce Business Model Right for You?
Although online retail is a super-large market and there’s a lot of money to be made in it, it comes with some administrative responsibilities.
From sourcing for products to keeping an inventory to shipping out orders, you can expect to get physically tuckered out if you work alone perpetually.
The solution might be to outsource the packaging and shipping process or adopt a dropshipping model. But just keep in mind that this will directly translate into added handling fees and ultimately more upfront investment.
Additionally, depending on the product and the standards of the industry you’re in, you may be forced to keep your markup low to stay competitive in pricing. The eCommerce model congenitally comes with lots of overheads, which means more fangs eating into your final profit margin.
For clarity, the major way revenue is generated with physical products is by placing markup on the original cost of the product to achieve a profit margin.
In summary, retailing physical products on the web is a great business model but the process of producing or procuring the product as well as the storage, packaging, marketing, and shipping can be costly, effort-intensive, and time-consuming. If you can deal with this, then it’s yours to take.
6. Software-based Business Model
If you’re able to create software-based products — such as web applications, mobile apps, desktop apps, cloud-based SaaS products, and the like — then this can be a worthwhile online business to start.
The archetypal thinking is that you build the product once and keep selling it to multiple users. They either download it, access it in the cloud, or install it in their virtual environment.
Just as physical products, you could sell your software or web-based products through a third-party platform that has ready-to-buy traffic but takes a cut of your profits. Think of the Apple App Store or Google Play Store as examples:

Howbeit, selling directly from your website or social media means you get to keep the money but drive your own traffic.
Software and web-based solutions can be sold as a one-off or on a subscription basis.
Examples of Software-based Business
- Artificial intelligence tools
- SaaS and cloud products
- Mobile apps
- Plugins or add-ons for popular software platforms
- Desktop software
- Web-based marketplace platforms
Is the Software-based Business Model Right for You?
As I said, the software model is a tempting business model being that you create one software and then sell it to multiple people over and over.
However, creating software-based products is often time-consuming and requires high-level technical knowledge.
For instance, to create software, you have to know how to code. It’s possible to learn to code, but it takes months. Hiring a programmer to do it for you comes with high costs.
And after creating your software, you have to spend money and time testing, patching and regularly updating it. And of course, you usually would have to provide technical support to users, year in and year out.
This is not ideal for most people.
To illustrate, Scalenut is an incredibly powerful content and SEO software with a bunch of great features. It’s useful. People love it. But it probably took the developers months and months of hard work to get it created and perfected to its current standard.
And the company is still putting a good deal of resources into maintaining it.
Personally, I think selling software or a web-based solution is a great way to generate revenue. If you’re ready to deal with the work associated with it, then this can be a viable option for you.
7. Virtual Assets Business Model
While not a traditional online business model like the above-mentioned ones, this business model heavily relies on online platforms, thus making it an integral part of the digital economy. This model involves the creation, distribution, and exchange of virtual assets, which can include currencies, cryptocurrencies, metaverse-related assets such as virtual lands, and other digital assets like stablecoins and non-fungible tokens.
It is a rapidly evolving and highly volatile market that is driven by various factors such as supply and demand, investor sentiment, regulatory developments, and technological advancements.

The virtual assets business model is still in its early stages of development, but it has the potential to revolutionize the way we interact with and exchange value online. This model is already disrupting a number of industries, including finance, gaming, and collectibles.
This economy attracts a diverse range of participants, including retail investors, institutional investors, HODLers, traders, developers, and entrepreneurs.
One major benefit of this business model is the potential for high returns on investment. Digital assets are known for their volatility, which means that prices can rise and fall rapidly, offering opportunities for traders and investors to profit from price movements.
Examples of Virtual Assets Businesses
- Day trading/swing trading
- Dollar-cost averaging for bullish markets
- Developing your own project (coin, token, etc.)
- Crypto exchanges
- Metaverse
- Non-fungible tokens (NFTs)
- DeFi
- GameFi
- Investing in virtual lands
Is the Virtual Assets Business Model Right for You?
The virtual assets business model can be both rewarding and risky.
For instance, the blockchain market is relatively new and unregulated, which can result in high levels of volatility and uncertainty. As a result, there is a potential for large gains, but also for significant losses.
In addition, trading or investing in digital assets requires a certain level of technical knowledge and expertise, which can be a barrier to entry for some individuals. Without the necessary understanding, investing in digital assets can be risky and may result in losses.
Despite these risks, digital asset-based businesses can be a lucrative opportunity for those with a high-risk tolerance and a willingness to learn and adapt to a rapidly changing market.
In Summary:
The whole concept of making money online comes down to seven universal online business models as discussed above.
They all are highly implementable. They all make money. They all have their strengths and weaknesses.
Ultimately, the choice of which online business model to pursue should be based on your own interests and goals.











